What is Gum Disease?
Gum disease describes bleeding, red, or swollen gums. It begins with hard and soft deposits on the surfaces of the teeth. If left untreated, bacterial build-up called plaque collects at the gum line. This plaque buildup eventually hardens into tartar or calculus.

When poor oral care is present, bacteria cause inflammation of the gums (gum disease / gingivitis). Over time, these bacteria can spread into the bone, resulting in a condition called periodontitis. Left treated, periodontal disease leads to the complete destruction of the tooth’s supporting tissues, abscesses and, ultimately, loss of the tooth.
Signs and Symptoms (Source: The Canadian Dental Hygienists Association)
● Red, swollen or tender gums
● Bleeding while brushing or flossing
● Gums that pull away from the teeth
● Persistent bad breath
● Loose or separating teeth
● A change in the way your teeth fit together





 Gum inflammation is a common term used to refer to gingivitis. Gingivitis describes an oral condition where the gums have become swollen and inflamed, hence the term gum inflammation. In addition to inflamed gums, the gums also bleed easily when touched, brushed or flossed. The gums are light pink or pinkish-red in health, but they take on a red appearance when gingivitis is present.
Gum inflammation is a common term used to refer to gingivitis. Gingivitis describes an oral condition where the gums have become swollen and inflamed, hence the term gum inflammation. In addition to inflamed gums, the gums also bleed easily when touched, brushed or flossed. The gums are light pink or pinkish-red in health, but they take on a red appearance when gingivitis is present. as your dentist or dental hygienist ever told you during your dental visit that you have bleeding gums? Bleeding gums are one symptom of gum disease, commonly referred to as gingivitis. You may have noticed that your gums bleed while you brush or floss your teeth at home.
as your dentist or dental hygienist ever told you during your dental visit that you have bleeding gums? Bleeding gums are one symptom of gum disease, commonly referred to as gingivitis. You may have noticed that your gums bleed while you brush or floss your teeth at home.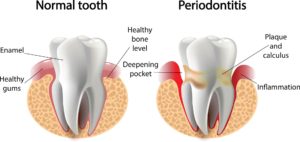 Periodontal disease is another term used when referring to periodontitis. Unlike gingivitis, a type of reversible gum disease, periodontitis is not reversible. Periodontal disease involves the permanent breakdown of gum tissue and bone in the mouth.
Periodontal disease is another term used when referring to periodontitis. Unlike gingivitis, a type of reversible gum disease, periodontitis is not reversible. Periodontal disease involves the permanent breakdown of gum tissue and bone in the mouth.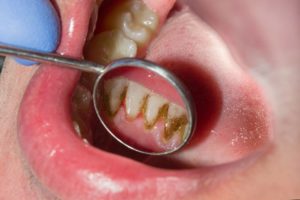 Dental plaque is a film of bacteria that forms on the teeth. It has a sticky feel, and it is colourless. It is very noticeable to your tongue’s touch when you have not brushed your teeth.
Dental plaque is a film of bacteria that forms on the teeth. It has a sticky feel, and it is colourless. It is very noticeable to your tongue’s touch when you have not brushed your teeth.